Introduction to Computer
One of the most visible developments in recent decades has been the introduction of computers. A computer is now a regular equipment, and we are all familiar with its applications in numerous sectors. Computers are utilised for everything from basic operations like printing letters to complicated weapon design work. Intelligent devices can be found in train stations, airports, supermarkets, banks, manufacturing plants, and even at home. People of many ages utilise computers for a variety of purposes. Computers have spawned new eras in finance, sales, and education. To succeed in his or her own area, each person must have a fundamental understanding of computers, regardless of the sector in which he or she works. As a result, knowing how to use a computer is essential for everyone.One should be able to grasp computer operation and use it in his or her field of work. One must have a fundamental grasp of the Internet, WWW, and its applications. In summary, you must understand how to employ computer power in your sector to get the most out of it. Without it, your competition will constantly be one step ahead of you, leaving you in the dust. In today's information-technology environment, success in any market area is determined by the quality of information possessed. A corporation that is up to date on the newest developments in its industry and rivals will be able to prepare more effectively. In this sense, success is dependent on knowledge and its use in planning and implementation. Computers and the internet can give up-to-date information and analyse it in such a manner that it is useful to enterprises.
We live in a world that is entirely controlled by computers. ATM machines and online banking allow you to conduct financial transactions from the comfort of your own home. You can book a train or an airline ticket from your computer. You may access your exam results over the internet. You may file your income tax returns from the comfort of your own home. You may look for clients for your items all around the world. You may buy a variety of items on the internet. On the internet, you may read numerous books and listen to music. All of this is only feasible if you know how to use a computer and the internet.
Several new fields of research have been discovered thanks to the use of computers. Some disciplines, such as robotics, artificial intelligence, mobile telephony, satellite communication, computer-controlled weaponry, DNA research, and nanotechnology, could not exist without computers. In the previous 50 years, the computing industry has been one of the key industries in which the world has invested the most money in research.
You may believe that computers are tough to understand and that computer programmes are difficult to execute. This fear will stay with you until you begin learning about computers. When you begin learning and using the principles, you will discover that the fundamental computer applications are quite simple to understand and use. This book is intended to assist you in understanding the fundamentals of computers as well as a few popular computer programmes.
WHAT IS COMPUTER?
A computer is a piece of electronic equipment. It is used to transform a meaningless collection of facts into meaningful data. "Data Processing" refers to the process of transforming useless data into meaningful information. The user issues orders to the computer, and the machine executes them. The actions performed by computers are extremely fast and precise. Computers continue to do the same work with the same efficiency and in the same amount of time. They are not impacted by tiredness by executing the same operations again. Computers contain massive amounts of memory to store information for later use.
Take a look at the diagram below, which represents a personal computer and its essential components. The computer's major components are the display, system unit, keyboard, and mouse. The output is displayed by the monitor or Visual Display Unit, the input is provided by the keyboard and mouse, and the system unit is in charge of processing the input to create the output. It is critical to note that the system unit is not a CPU (Central Processing Unit). The CPU is a device that is part of the system unit and is responsible for real data processing. Most people refer to the system unit as the CPU, which is incorrect.
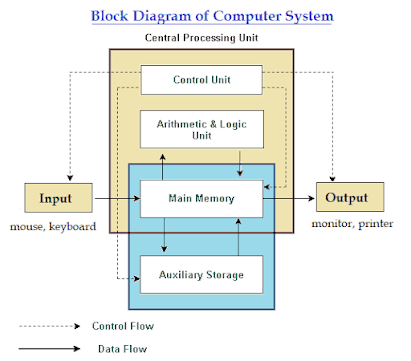
Block Diagram of Computer
Hardware refers to the physical components of a computer system that are utilised to process data. Computers, regardless of their design or size, conduct the five fundamental processes listed below to turn raw input data into information valuable to users.
- Inputting : The process of entering data and instructions into computer system is called Inputting
- Storing : Saving data and instructions so that they are available for future use whenever required.
- Processing : Performing arithmetic operations (Add, Subtract, Multiply, Divide etc.) or logical operations (Comparisons like equal to, less than, greater than etc.) on data in order to convert them into useful information.
- Outputting : The process of obtaining useful information or results to user such as printed report or visual display.
- Controlling : Detecting the manner and sequence in which all above operations are performed.
- Input Unit: The input units are the input devices connected to a system that allow users to provide instructions for the computer to execute. These devices include the mouse, keyboard, scanner, and so on. These devices provide as a way of communication between the user and the system. The computer receives the input as binary (machine-readable) raw data and conducts the necessary processing. When the processing is finished, it outputs the results to output devices such as displays, printers, and so on.
- Central Processing Unit(CPU): The CPU is the computer's brain/heart. The CPU is the heart of the computer. The CPU processes all instructions sent to the computer by the user. The CPU receives input from the user or a set of instructions and creates output in response. It is a piece of electrical gear that conducts all arithmetic and logical operations. It is in charge of activating and managing the operation of the other components.
Block Diagram of CPU:
CPU consists of two major componentsArithmetic Logic Unit: All arithmetic and logical operations are done in this section of the CPU. The arithmetic part does arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, while the logical section performs logical operations such as AND, OR, Equal, Less than, Greater than, and so on. Logical is also in charge of processes like comparing, matching, and selecting.
Control Unit(CU): Based on the name, we may deduce that the control unit (CU) is in charge of all actions or operations carried out within the computer system. As seen in the picture above, the control unit is linked to the system's memory unit, which means it gets instructions or information directly from the computer's main memory. The control unit translates those instructions into a collection of signals, which it then sends to another portion of the computer system for processing.
- Memory Unit: The memory unit, often known as a storage unit, is a significant component of a computer system or component of a digital computer. The data and instructions are saved in a memory unit for further processing after and before it. This unit stores the intermediate and final findings. The instructions are sent from the memory unit to other elements of the system.
Memory units are classified into two types:Primary Storage Unit: The temporary data or command is stored in main memory. They are not capable of storing large amounts of data. It is used to save the presently executed instruction or the immediate computation result. The data in this primary will be lost if the computer's power is turned off. It is sometimes referred to as Main memory or Temporary memory. RAM is one example of this form of memory (Random Access Memory).
Secondary Storage Unit: When we need to save data permanently for future processing, we employ the computer's secondary memory. It is the polar opposite of primary memory. Even if the power source dies, the data is not lost. It is sometimes referred to as secondary storage, supplementary storage, or permanent storage. A hard disc or solid-state drive (SSD) is an example of this form of memory (Solid-state drive) - Output Unit: The output unit is the computer system's third and final component. Data is translated into a format that people can understand after it has been processed. The data is displayed to users via the output units after conversion. Monitors, displays, printers, and speakers are examples of output devices.
INTERACTION OF VARIOUS COMPUTER COMPONENTS
- The input unit receives user input and routes it to the CPU.
- These instructions are stored in main memory by the CPU. Some of these instructions may be saved in secondary memory as well.
- Data is transferred from secondary memory to main memory for execution.
- The CPU reads instructions from main memory.
- ALU is responsible for arithmetic and logical computations. It is overseen by CU.
- The results of the calculations are saved in main memory.
- If any faults occur, they are presented on the output unit.
- The results are passed from the main memory to the output unit.